With the unemployment rate at 4 percent or below for eight consecutive months, 2018 appears to be the year when the economy finally became healthy again after the Great Recession. But while low unemployment is good news, the fruits of economic growth are largely bypassing typical families and going straight into the hands of the already-rich.
EPI’s Top Charts of 2018 tells the story of how working people are doing in today’s economy. After a slow recovery from the Great Recession, we are quickly resuming our prerecession course of rising inequality. By weakening workers’ ability to collectively bargain, refusing to raise a stagnant federal minimum wage, and giving out tax breaks to the richest Americans, policymakers have contributed to this increasing economic divide.
However, the data also show that progressive policies intended to help working people actually do allow them to achieve a higher standard of living. When states like Minnesota boost public investment in education, raise the minimum wage, and increase labor standards, wages and employment grow. Likewise, data show that raising the tipped minimum wage to the regular minimum wage helps reduce the number of workers in poverty.
EPI’s Top Charts of 2018 tells the story of the year in images. The 12 charts and maps are interactive, embeddable, and can be easily shared on social media.
View all 12 charts on epi.org.
Depending on the state, the average top 1-percenter makes between 12.7 and 44.4 times more each year than the average bottom 99-percenter
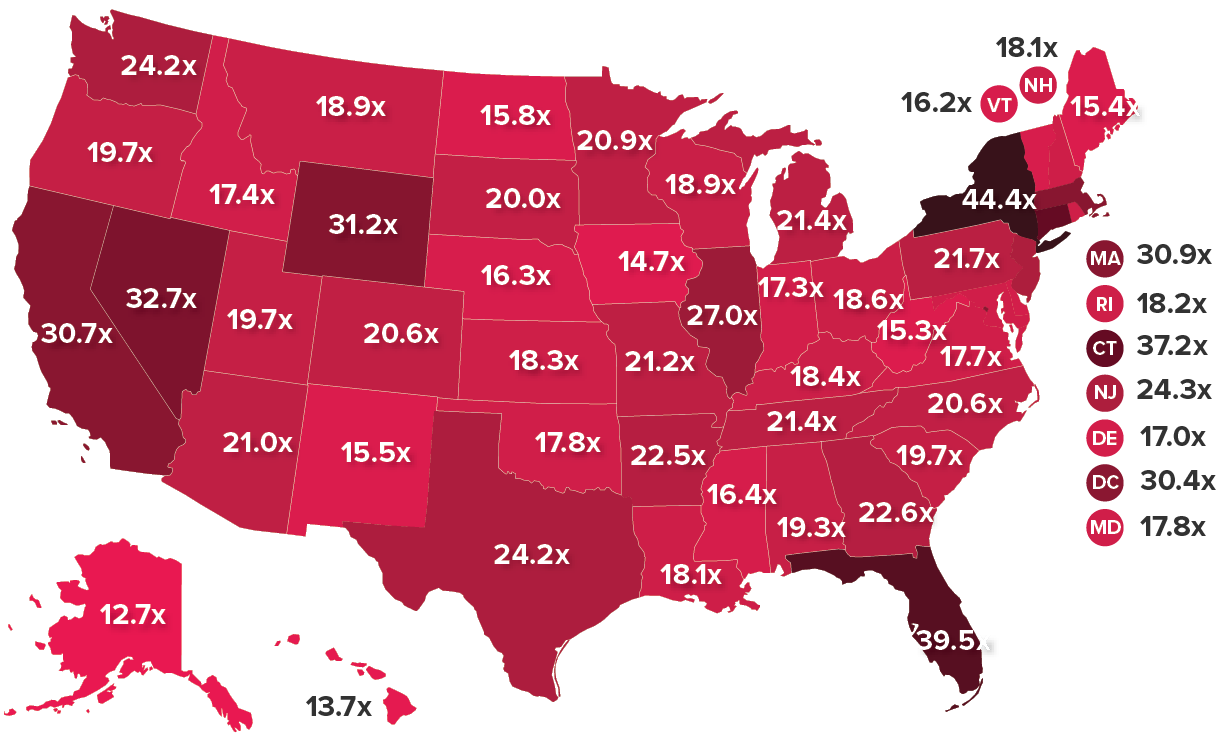
Source: Estelle Sommeiller and Mark Price, The New Gilded Age: Income Inequality in the U.S. by State, Metropolitan Area, and County, Economic Policy Institute, July 2018. Map is based on 2015 income data for tax units.
Attacks on unions have hurt their ability to hold inequality in check: Union membership and share of income going to the top 10 percent, 1917–2015
| Year | Union membership | Share of income going to the top 10 percent |
|---|---|---|
| 1917 | 11.0% | 40.3% |
| 1918 | 12.1% | 39.9% |
| 1919 | 14.3% | 39.5% |
| 1920 | 17.5% | 38.1% |
| 1921 | 17.6% | 42.9% |
| 1922 | 14.0% | 42.9% |
| 1923 | 11.7% | 40.6% |
| 1924 | 11.3% | 43.3% |
| 1925 | 11.0% | 44.2% |
| 1926 | 10.7% | 44.1% |
| 1927 | 10.6% | 44.7% |
| 1928 | 10.4% | 46.1% |
| 1929 | 10.1% | 43.8% |
| 1930 | 10.7% | 43.1% |
| 1931 | 11.2% | 44.4% |
| 1932 | 11.3% | 46.3% |
| 1933 | 9.5% | 45.0% |
| 1934 | 9.8% | 45.2% |
| 1935 | 10.8% | 43.4% |
| 1936 | 11.1% | 44.8% |
| 1937 | 18.6% | 43.3% |
| 1938 | 23.9% | 43.0% |
| 1939 | 24.8% | 44.6% |
| 1940 | 23.5% | 44.4% |
| 1941 | 25.4% | 41.0% |
| 1942 | 24.2% | 35.5% |
| 1943 | 30.1% | 32.7% |
| 1944 | 32.5% | 31.5% |
| 1945 | 33.4% | 32.6% |
| 1946 | 31.9% | 34.6% |
| 1947 | 31.1% | 33.0% |
| 1948 | 30.5% | 33.7% |
| 1949 | 29.6% | 33.8% |
| 1950 | 30.0% | 33.9% |
| 1951 | 32.4% | 32.8% |
| 1952 | 31.5% | 32.1% |
| 1953 | 33.2% | 31.4% |
| 1954 | 32.7% | 32.1% |
| 1955 | 32.9% | 31.8% |
| 1956 | 33.2% | 31.8% |
| 1957 | 32.0% | 31.7% |
| 1958 | 31.1% | 32.1% |
| 1959 | 31.6% | 32.0% |
| 1960 | 30.7% | 31.7% |
| 1961 | 28.7% | 31.9% |
| 1962 | 29.1% | 32.0% |
| 1963 | 28.5% | 32.0% |
| 1964 | 28.5% | 31.6% |
| 1965 | 28.6% | 31.5% |
| 1966 | 28.7% | 32.0% |
| 1967 | 28.6% | 32.0% |
| 1968 | 28.7% | 32.0% |
| 1969 | 28.3% | 31.8% |
| 1970 | 27.9% | 31.5% |
| 1971 | 27.4% | 31.8% |
| 1972 | 27.5% | 31.6% |
| 1973 | 27.1% | 31.9% |
| 1974 | 26.5% | 32.4% |
| 1975 | 25.7% | 32.6% |
| 1976 | 25.7% | 32.4% |
| 1977 | 25.2% | 32.4% |
| 1978 | 24.7% | 32.4% |
| 1979 | 25.4% | 32.3% |
| 1980 | 23.6% | 32.9% |
| 1981 | 22.3% | 32.7% |
| 1982 | 21.6% | 33.2% |
| 1983 | 21.4% | 33.7% |
| 1984 | 20.5% | 33.9% |
| 1985 | 19.0% | 34.3% |
| 1986 | 18.5% | 34.6% |
| 1987 | 17.9% | 36.5% |
| 1988 | 17.6% | 38.6% |
| 1989 | 17.2% | 38.5% |
| 1990 | 16.7% | 38.8% |
| 1991 | 16.2% | 38.4% |
| 1992 | 16.2% | 39.8% |
| 1993 | 16.2% | 39.5% |
| 1994 | 16.1% | 39.6% |
| 1995 | 15.3% | 40.5% |
| 1996 | 14.9% | 41.2% |
| 1997 | 14.7% | 41.7% |
| 1998 | 14.2% | 42.1% |
| 1999 | 13.9% | 42.7% |
| 2000 | 13.5% | 43.1% |
| 2001 | 13.5% | 42.2% |
| 2002 | 13.3% | 42.4% |
| 2003 | 12.9% | 42.8% |
| 2004 | 12.5% | 43.6% |
| 2005 | 12.5% | 44.9% |
| 2006 | 12.0% | 45.5% |
| 2007 | 12.1% | 45.7% |
| 2008 | 12.4% | 46.0% |
| 2009 | 12.3% | 45.5% |
| 2010 | 11.9% | 46.4% |
| 2011 | 11.8% | 46.6% |
| 2012 | 11.2% | 47.8% |
| 2013 | 11.2% | 46.7% |
| 2014 | 11.1% | 47.3% |
| 2015 | 11.1% | 47.8% |
Source: Figure A in Celine McNicholas, Samantha Sanders, and Heidi Shierholz, First Day Fairness: An Agenda to Build Worker Power and Ensure Job Quality, Economic Policy Institute, August 2018.
Source: Figure A in Celine McNicholas, Samantha Sanders, and Heidi Shierholz, First Day Fairness: An Agenda to Build Worker Power and Ensure Job Quality, Economic Policy Institute, August 2018. Data on union density follows the composite series found in Historical Statistics of the United States; updated to 2015 from unionstats.com. Income inequality (share of income to top 10 percent) data are from Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez, “Income Inequality in the United States, 1913–1998,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 118, no. 1 (2003) and updated data from the Top Income Database, updated June 2016.